Legitimately Worried That You’re Being Targeted Online? Try Lockdown Mode
Most people fall into one of two extremes when it comes to device security. Many believe they’re not interesting enough to be targeted by online attackers and thus don’t take sensible precautions, like making sure every website account is protected with a strong, unique password. (Most attacks these days are bots, so whether you’re interesting is irrelevant.) Then there are those who see a bogeyman around every corner and refuse to use a password manager or biometric authentication because of misplaced concerns about the security of the stored data. (Really, it’s OK.)
Today we want to focus instead on a very small third group: those who, because of who they are or what they do, have a legitimate reason to fear being targeted by sophisticated digital attacks. Such people might include activists trying to raise awareness about human rights abuses in oppressive regimes, political dissidents, muckraking journalists covering organized crime or government corruption, senior executives in controversial business fields, high-profile government officials, and government employees with access to sensitive information.
For such people, using a password manager and relying on biometric authentication is table stakes. Government intelligence and law enforcement agencies often employ hacking software like Pegasus, which can be installed on target iPhones through zero-click exploits such as simply receiving a malicious text message. Pegasus can read text messages, snoop on calls, collect passwords, track location, access the iPhone’s camera and microphone, and harvest information from apps. Plus, both government agencies and organized crime rings employ hackers to target high-profile targets directly, often through social engineering (pretending to be someone they’re not to gain access to an account or device).
Apple is well aware of the risk to high-value individuals. In November 2021, the company filed a lawsuit against Pegasus maker NSO Group. More practically, Apple introduced Lockdown Mode in iOS 16, iPadOS 16, and macOS 13 Ventura, significantly reducing the attack surface that spyware or hackers could exploit by limiting or blocking specific apps, websites, and features.
Lockdown Mode Limitations
Before we explain how to turn on Lockdown Mode, it’s vital that you understand how it limits your Apple devices:
- Messages: Most message attachment types are blocked other than certain images, video, and audio. Lockdown Mode also blocks links and link previews.
- Web browsing: Safari blocks complex Web technologies, potentially causing some websites to load slowly or not operate correctly. It may also block Web fonts and images, so sites may not display as designed.
- FaceTime: Incoming FaceTime calls are blocked unless you have previously called that person.
- Apple services: Invitations to Apple services, such as invitations to join the Home app, are blocked unless you have previously invited that person.
- Shared albums: Shared albums disappear entirely from the Photos app, and shared album invitations are blocked.
- Device connections: If you want to connect an iPhone or iPad to a computer or accessory, the device must first be unlocked. Similarly, connecting an M-series Mac laptop to an accessory requires explicit approval.
- Configuration profiles: Lockdown Mode prevents you from installing configuration profiles, and the device can’t be enrolled in Mobile Device Management.
The inconvenience these restrictions create is well worth the protection Lockdown Mode provides if you’re a sufficiently high-value target. But for the vast majority of Apple users, Lockdown Mode’s limitations would just cause confusion and annoyance.
Turning on Lockdown Mode
First, note that you must enable Lockdown Mode on each of your devices separately.
To enable Lockdown Mode on an iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Lockdown Mode (at the bottom) and tap Turn On Lockdown Mode on two separate screens. For the last step, tap Turn On & Restart, and enter your passcode.
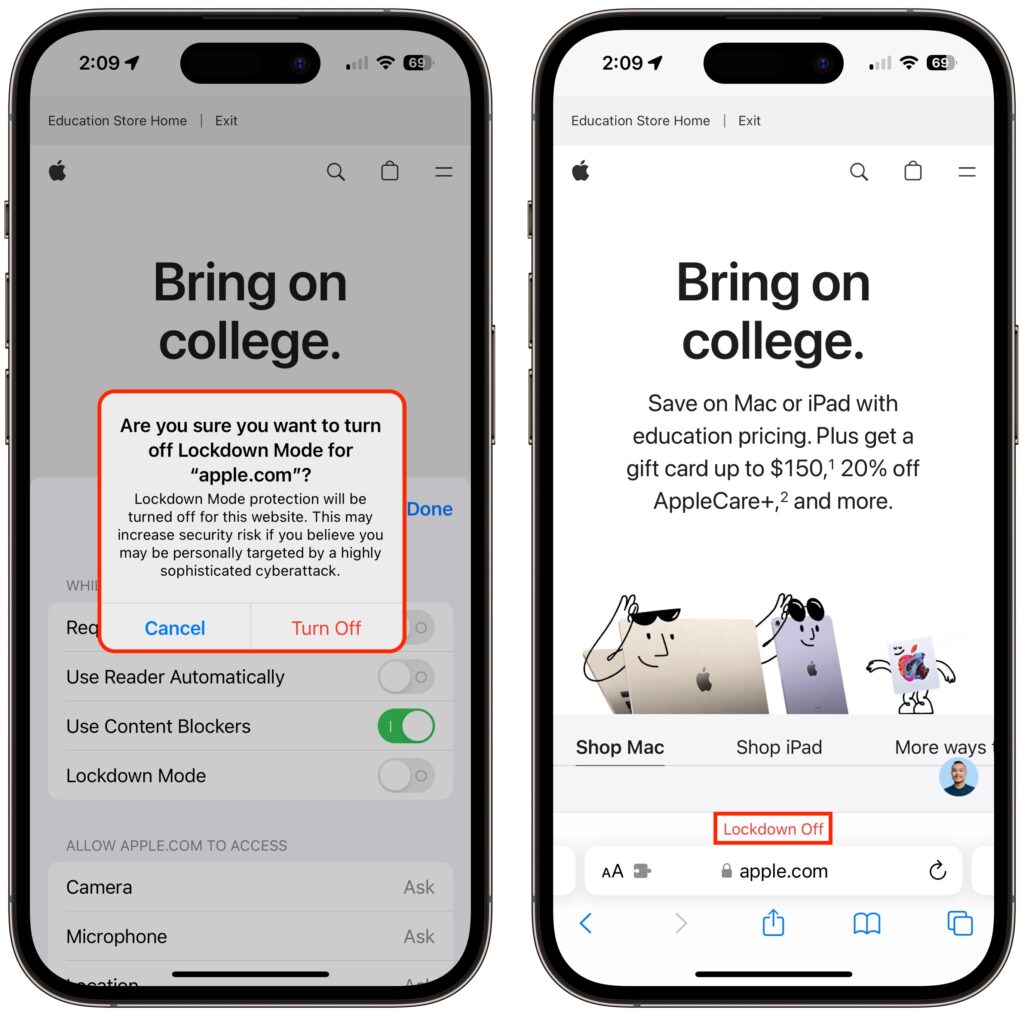
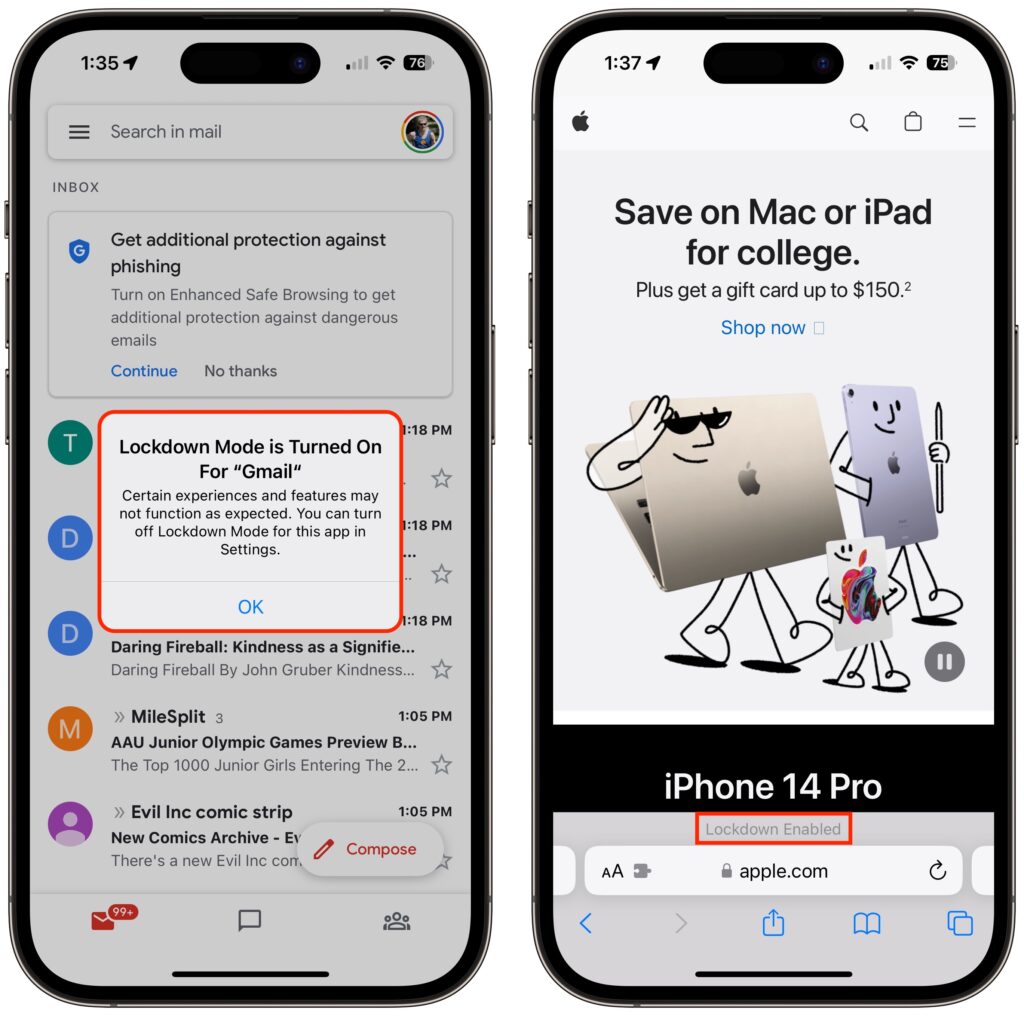
Once your iPhone restarts, it will work mostly the way you expect, apart from the above limitations. You may see notifications when an app has been limited in some way, and a banner appears in Safari to let you know you’re in Lockdown Mode.
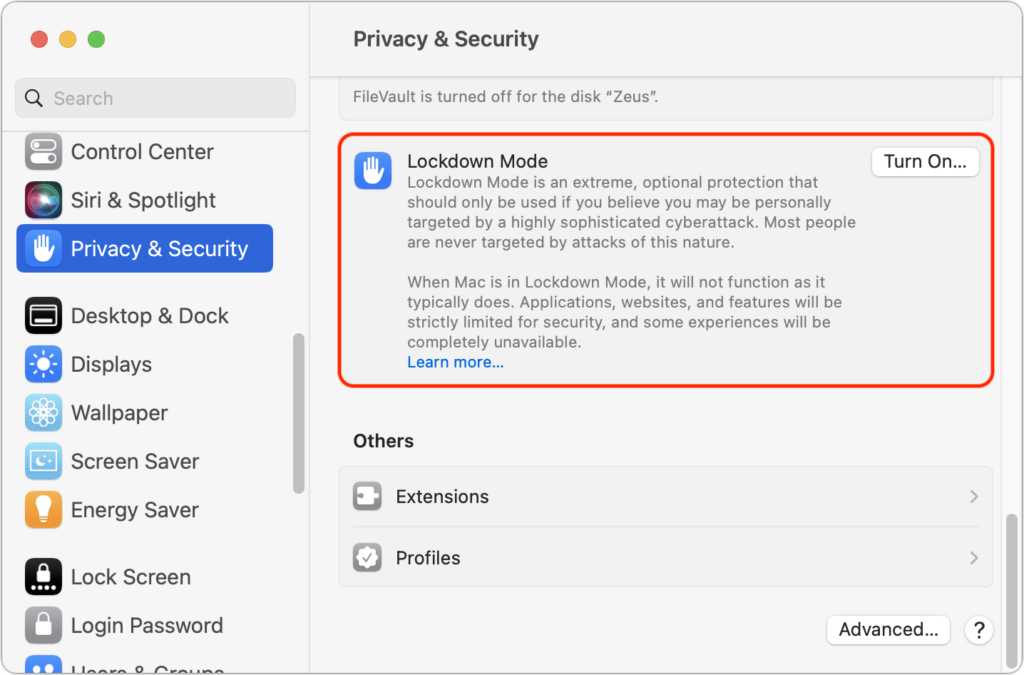
On a Mac, turn on Lockdown Mode by going to System Settings > Privacy & Security. Scroll down to Lockdown Mode and click Turn On. Authenticate, then click Turn On & Restart.
As with the iPhone and iPad, Lockdown Mode mainly makes its presence known by displaying a banner in Safari; you may also receive notifications when an app or feature is limited.
Allow Certain Apps or Websites in Lockdown Mode
If you discover that a particular app or website isn’t operating correctly in Lockdown Mode, you can exclude it from Lockdown Mode’s protections. You’ll have to decide if it’s worth the added risk. To manage exceptions on the iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Lockdown Mode. Then scroll to the bottom, tap Configure Web Browsing, and on the next screen, turn off the switch for the desired app.
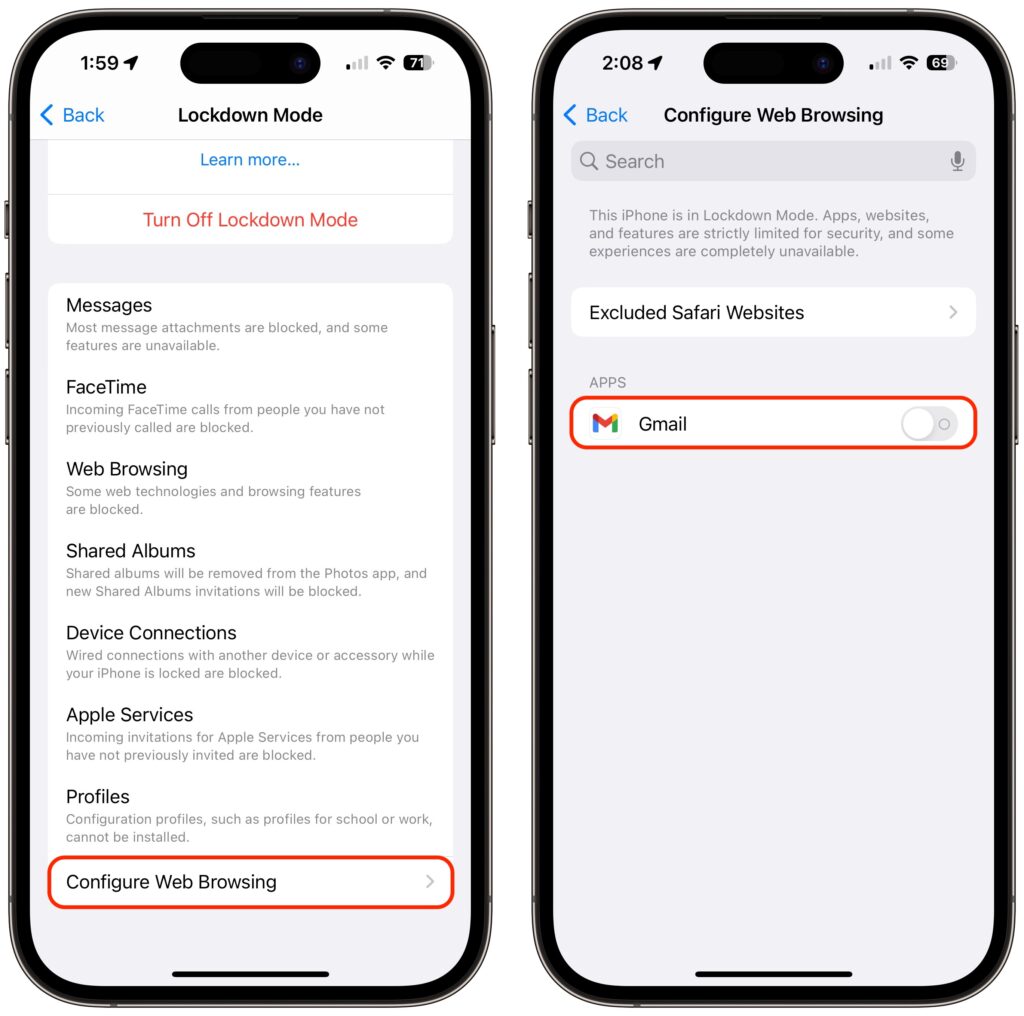
To exclude websites from Lockdown Mode, use Safari. Tap the AA button in the address bar, disable the Lockdown Mode switch, and tap Turn Off. The Lockdown banner changes to Lockdown Off to make sure you know that website is no longer being limited for your protection.

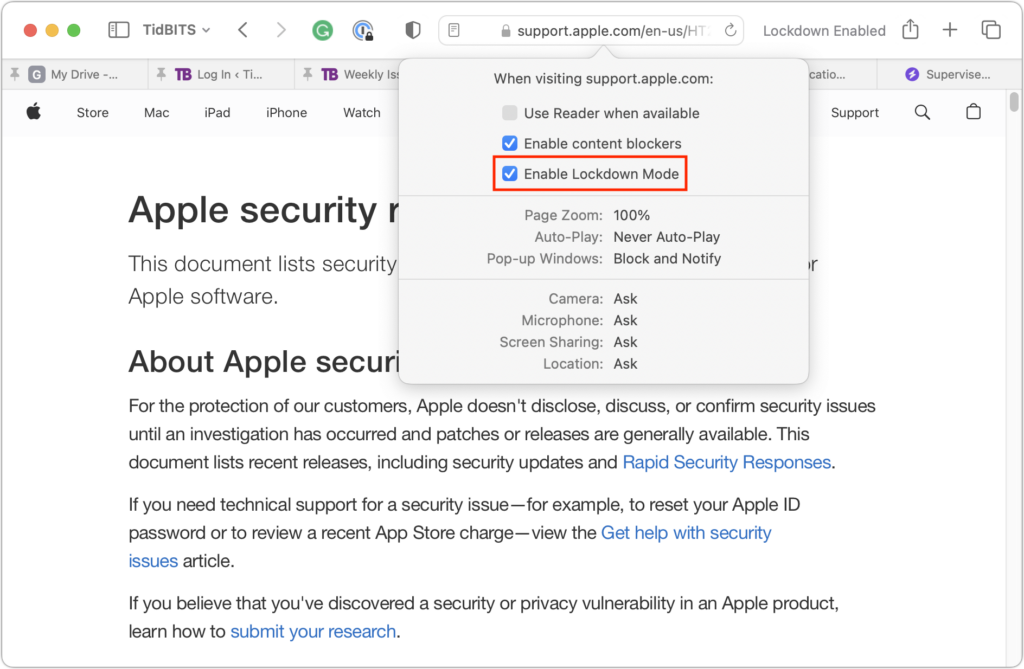
On the Mac, you can exclude websites in Safari, but not apps. While on the site you want to exclude, choose Safari > Settings for website.name. In the popover that appears, deselect Enable Lockdown Mode and then click Turn Off when prompted.
To reiterate, almost no one needs to enable Lockdown Mode. But if you qualify as a high-value target, it’s well worth using Lockdown Mode to reduce the chances that powerful forces will be able to compromise your iPhone, iPad, or Mac.
(Featured image based on originals by iStock.com/Tero Vesalainen and matias giamportone)
Social Media: High-value targets like activists, journalists, and government employees with access to sensitive information should consider enabling Lockdown Mode on their Apple devices to protect against hacking or spying by sophisticated digital attackers.